Diet therapy plays a key role in the fight against obesity, and the main principle is significant calorie restriction. Today, our AnabolShop.org team has prepared a unique article for you that will reveal the topic and secrets of effective, fast, and, most importantly, safe weight loss for everyone! Enjoy reading!
Determining the degree of calorie restriction. The degree of calorie restriction should be proportional to the degree of excess weight. The greater the excess weight, the more stringent the calorie restriction should be.
Calculating the required calorie intake:
- Determining normal body weight. First, it is necessary to determine the normal body weight for a specific person, considering their height, gender, and age.
- Calculating the energy value. Based on normal body weight, the required number of calories to maintain the body's vital functions is calculated.
- Calorie reduction in obesity: In severe obesity, calorie intake should be reduced by 40% of normal requirements. Depending on individual characteristics and the effectiveness of treatment, this percentage can vary from 30 to 50%.
When planning a diet, it is important to consider the patient's energy expenditure during standard physical activity. This will allow for a more accurate determination of the required number of calories and ensure effective weight loss.
For people striving for optimal weight, having an accurate assessment tool is crucial. While there are various methods for determining ideal body weight, Broca's formula, based on a simple calculation of "height in centimeters minus 100," is only an approximate guide.
More accurate methods:
For a more detailed assessment, specialized tables that consider height, build, and weight can be used. However, one of the most advanced approaches is the A.A. Pokrovsky nomograph. This tool, which considers five factors—height, gender, age, occupation, and body composition – allows for highly accurate determination of an individual's ideal body weight and daily requirement for essential nutrients.
Increasing the body's energy expenditure through physical activity is a crucial part of obesity treatment. This involves more than just random exercise, but a carefully designed and monitored physical activity program. Such programs involve a gradual increase in both the frequency and difficulty of exercises.
Synergistic effect: It's the combination of a balanced diet and properly selected exercise that yields the best results. This comprehensive approach leads not only to a reduction in fat mass but also, importantly, to an increase in active muscle mass. This is confirmed by densitometric weighing data, a method that accurately determines body composition.
The result is not just weight loss, but also improved overall health, increased tone, and a change in body composition toward a healthier muscle-to-fat ratio.

Brief Historical Background:
Therapeutic nutrition systems similar to "Table No. 8" were developed in the 1920s in the USSR by Soviet scientist M. I. Pevzner. The main goal of such diets is to treat obesity by limiting calories, fats, and carbohydrates, as well as salt, sugar, and fluid intake.
Historical Roots:
These diets originated in the Soviet Union and have no connection to the cuisines of other countries. This therapeutic diet is designed for people suffering from obesity, with the goal of losing weight and improving overall health.
Key Principles:
- Limiting salt, sugar, and fluid intake.
- Eliminating or significantly limiting foods that stimulate appetite.
- Using sugar substitutes instead of sugar.
Differences from other diets:
These dietary systems are not related to diets typical of other countries, including the Mediterranean cuisine that developed in Greece, Italy, Spain, and France.
Balance and stimulation of lipolysis
The key to developing a weight loss diet is the principle of a balanced diet. This means including foods rich in:
- Essential amino acids
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)
- A full spectrum of vitamins
Regarding optimal protein intake, protein plays a critical role in maintaining health, and adequate (but not excessive) consumption is essential. Long-term protein restriction in the diet can negatively impact the functioning of:
- Liver
- Cardiovascular system
- Other vital organs
Fats, in turn, are allies in the fight against excess weight:
Contrary to popular belief, increasing the proportion of fats in the diet to 40-50% of total calories can be beneficial for normalizing:
- Lipolytic (fat breakdown)
- Liposynthetic (fat formation) processes.
Research shows that increasing fat intake activates the body's lipolytic systems, promoting fat mobilization from fat stores.
Carbohydrate Control:
Easily digestible sugars (insulinogenic substances) should be excluded from the diet. They are quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and stimulate insulin release, promoting fat deposition. Instead, it is recommended to use polysaccharides, which are absorbed more slowly and do not cause sharp insulin spikes. For added sweetness, you can use:
- Xylitol
- Fructose
- Aspartame
- Other sweeteners are intended for therapeutic nutrition.
Reduced Diets and Individualized Approaches:
For obesity, special reduced diets with a calorie content of 700 to 1800 kcal are often recommended. It is important that the energy value and composition of the diet be individually tailored, taking into account the nomograph data (mentioned earlier), which allows one to determine the optimal nutrient requirements.
Adjusting the amount of bread and butter in your diet is a simple way to tailor your diet to your individual needs and the recommendations derived from the nomograph. This allows you to flexibly tailor your diet to your specific needs, achieving the best results.

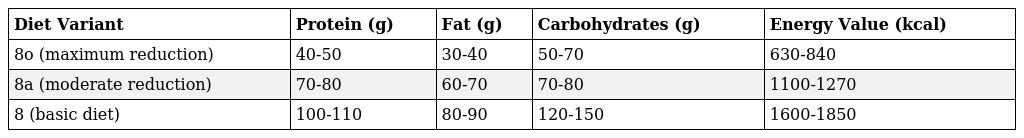
Reduced Diets for Obesity: Options and Principaqles
Various reduced diets, differing in energy value and macronutrient ratios, are used for effective treatment of obesity. The most common is Therapeutic Diet, which includes several sub-variants that allow the diet to be tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
It is recommended to begin treatment with the main Therapeutic Diet, which is characterized by a balanced composition and moderate calorie restriction. This option is often used in spa and outpatient settings.
Advantages of Therapeutic Diet:
- Good taste of dishes
- Sufficient total food volume
- High biological value
Particular attention is paid to:
- Seafood, rich in organic iodine and essential amino acids, low in carbohydrates.
- The complex protein product "Belip" (cottage cheese, cod, vegetable oil), which combines a balanced amino acid composition, unsaturated fatty acids, and vitamins.
Fasting days and special diets:
To enhance the effectiveness of treatment, it is recommended to include fasting days in the program, as well as special protein and fat days, designed to fit the patient's usual diet.
Basic principles of therapeutic nutrition for obesity:
- Reduced diet: Prescribe a low-energy diet.
- Carbohydrate restriction: Limit easily digestible carbohydrates (sugars).
- Animal fat restriction: Increase the proportion of vegetable fats (up to 50% of total fat) to activate lipolytic processes.
- Bulky foods: Create a feeling of satiety through low-calorie, but substantial food (raw vegetables, fruits, methylcellulose).
- Multiple meals: Eat multiple meals (up to 6 times a day) to satisfy hunger and avoid foods that stimulate the appetite (spicy snacks, spices).
- Normalize water and salt balance: Limit salt (up to 5g) and fluid (up to 1-1.5L).
- Dietary variations: Use contrasting fasting days.
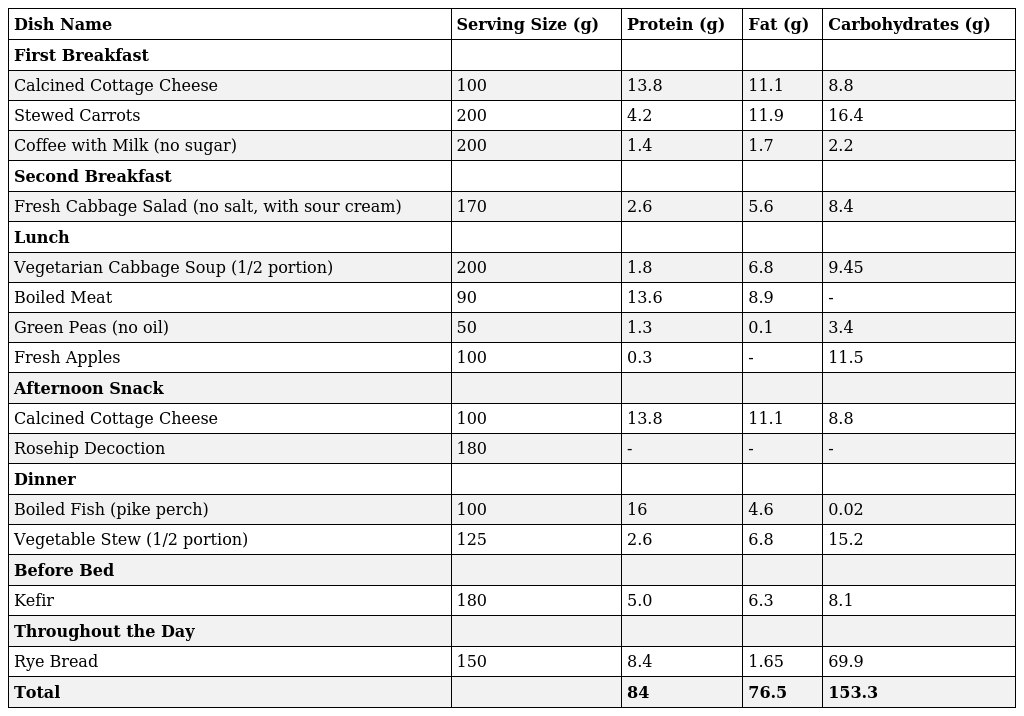
Sample Diet Menu for Obese Patients (1635 kcal)
Nutrition Tips and Approved Dishes for Obesity
Let's look at a list of recommended dishes and products to achieve the desired results for obesity:
1. Bread Products:
- Include up to 150 grams of black, high-protein wheat, or high-protein bread in your diet per day.
- Important! Monitor your weight and, if you're not losing weight, reduce the amount of bread you consume. Bread is the main source of carbohydrates, so adjusting its amount can help control weight loss.
2. First Courses – Soups:
- Give preference to soups made with vegetable broth.
- A light broth made with fish, meat, or mushrooms is acceptable no more than 2-3 times a week. Portion size: no more than half a plate.
3. Meat and Poultry Dishes:
- Choose lean beef; lean lamb or lean pork is allowed no more than twice every ten days. Cooking: Boil or jellied. Serving size: up to 150 grams per day. Include lean poultry, rabbits, and diet sausages in your diet.
4. Fish Dishes:
- Lean fish such as cod, pike perch, pike, navaga, or carp are recommended. Cooking: Boil, jellied, and occasionally fry. Fish can replace meat in a 1.5:1 ratio.
5. Protein Products:
- Remember! On average, you should consume 400 to 500 grams of protein products, such as meat, fish, and cottage cheese, per day. • To increase the biological value of your diet, add mussels, scallops, sea cucumbers, and squid, canned or raw, to your diet.
6. Vegetables and greens:
- Eat cabbage (cauliflower and white cabbage), cucumbers, radishes, lettuce, zucchini, and tomatoes in any form – raw, boiled, or baked.
- Eat potatoes, carrots, beets, and rutabagas in limited quantities – no more than 200 grams per day.
7. Cereals, legumes, and pasta:
- Limit your consumption of these foods. If you want to include them in your diet, reduce the amount of bread.
8. Eggs:
- Limit yourself to one egg per day.
9. Dairy products:
- Consume milk, yogurt, and kefir. Use sour cream as a topping for dishes, no more than 2 tablespoons.
- Include cottage cheese (preferably low-fat) in your diet – 100 to 200 grams per day in its natural form, in the form of tvorog pancakes, syrniki, or puddings. Mild cheeses are allowed.
10. Fruits and Berries:
- Include sweet-and-sour or sour fruits and berries, such as oranges, lemons, apples, gooseberries, red currants, and cranberries, in your diet – up to 200 grams per day, raw or in sugar-free compotes.
11. Sauces and Spices:
- Use mild sauces made with vegetables, fish, meat, or mushroom broth. Sauces with root vegetables, vinegar, and tomato paste are also acceptable.
12. Snacks:
- Include vinaigrettes, salads, lean fish in aspic, bologna, and lean ham in your diet.
13. Drinks:
- Allowed are tea (including with milk), weak coffee, fruit juices from sour berries and fruits, tomato juice, and alkaline mineral water. Total daily fluid intake: up to 5 glasses (including drinks, soup, yogurt, milk, and compote).
14. Fats:
- Use up to 40 grams of butter or vegetable oil per day for cooking.
15. Salt:
- Daily salt intake: no more than 5 grams. Cook meals without salt.
Strictly prohibited!
Chocolate, candy, baked goods, ice cream, and other sweets, as well as spicy, salty, and smoked foods and snacks, peppers, horseradish, and alcoholic beverages.
Important! Treatment with a low-energy diet should be carried out while monitoring weight.
Remember! In addition to the main diet, it is necessary to have fasting days approximately once a week. On days with low physical activity, it is recommended to have meat-fasting days (up to 350 grams of boiled meat with a vegetable side dish, primarily cabbage) or cottage cheese days (up to 600 grams of cottage cheese with 2-3 cups of coffee or tea with milk without sugar). On rest days, apple (1,500 grams of apples), watermelon (up to 2 kg of watermelon pulp), milk (up to 6 cups), sour cream (up to 400 grams), or kefir (up to 1.5 liters) fasting days are suitable. Divide your meals into 5 meals throughout the day.
Caution! Complete fasting for 1-2 weeks, drinking only alkaline mineral water, is not an effective method for fighting obesity!

Very Important Aspects of Diet Therapy for Obesity:
Treating obesity with reduced-calorie diets requires systematic weight monitoring. It's important to understand that diet is only part of a comprehensive approach, and regular weighing helps evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen strategy and make timely adjustments.
Fasting Days:
To maintain weight loss momentum and prevent plateaus, it is recommended to have regular (approximately once a week) fasting days. The choice of fasting day type depends on your level of physical activity:
• For moderate physical activity:
- Meat fasting days: 280-350 g of boiled meat without salt with a vegetable (cabbage) side dish.
- Cottage Cheese fasting days: 500-600 g of cottage cheese with 2-3 glasses of tea or coffee with milk without sugar.
• Rest days:
- Apple fasting days: 1500 g of apples.
- Watermelon: 1.5-2 kg of watermelon pulp.
- Fermented milk: 1.5 liters of yogurt or kefir.
- Dairy: 5-6 glasses of milk.
- Sour cream: 300-400 g of sour cream.
It is important to distribute food evenly over 5 meals throughout the day.
Beware of extremes:
Complete fasting for 1-2 weeks, consuming only alkaline mineral water, is not an effective or safe method for treating obesity. Fasting can lead to muscle loss, slower metabolism, and other undesirable consequences.
Individual approach to concomitant diseases:
If you have concomitant diseases such as gout, atherosclerosis, or chronic cholangitis, your diet should be adjusted to suit the specifics of each condition:
- Exclusion: Meat and fish broths, as well as organ meats (offal), are completely excluded.
- Cooking Method: It is recommended to consume meat and fish primarily boiled.
- Alternative Protein Sources: Instead of meat and fish dishes, consider incorporating low-fat cottage cheese dishes into your diet more often, slightly limiting your overall protein intake.
If obesity is combined with gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, colitis):
- Exception: Vegetables with coarse plant fiber are excluded from the diet.
- Vegetable Preparation Method: Vegetables and greens should be consumed only boiled and mashed.
- Meat and Poultry: Meat, poultry, and fish (lean varieties) should be served boiled or steamed.
- Drinks: Strained compotes and kissels are recommended.
- Bread: Replace black bread with day-old white bread.
Interesting Fact: Inpatient treatment for obesity often uses Therapeutic Diet with a subsequent calorie reduction to 1200-1300 kcal (Therapeutic Diet). This allows doctors to more effectively monitor the patient's condition and achieve sustainable weight loss results.
Modified Diet Plan
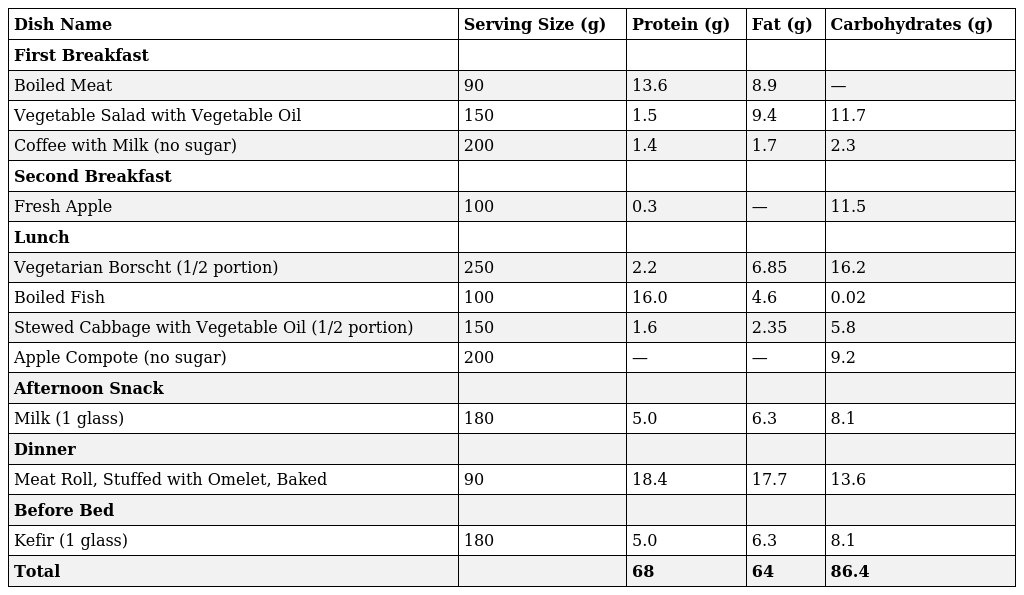
If the patient tolerates the diet satisfactorily, this diet is continued until weight loss is achieved. Once weight loss ceases, the patient is switched to a more restrictive diet (700-800 kcal).
It's important to understand that excessive calorie reduction can be dangerous. Reducing energy intake below a certain level, as in Diet 8a, is extreme. Further restriction can trigger ketosis and be detrimental to health.
The time limitations and conditions for prescribing this diet are that, due to the significant reduction in protein intake, it should only be prescribed for a short period (no more than 2-3 weeks) and only in a hospital setting under strict medical supervision.
Obesity treatment should begin with more moderate diets, avoiding drastic calorie reduction in the first few days. Intensive weight loss at the beginning of treatment is primarily due to fluid loss.
Criteria for the effectiveness of the treatment regimen:
Treatment effectiveness is assessed not only by weight loss but also by improvements in overall well-being and increased neuromuscular and mental tone.
The importance of physical activity:
All people who are overweight or have a tendency to gain weight should avoid resting immediately after eating.
The diet should be followed long-term, and the duration of dietary therapy is determined individually. It is important to understand that dieting alone without increased physical activity will not lead to significant weight loss.
Physical activity recommendations:
In addition to the therapeutic exercises prescribed by your doctor, the following is recommended:
- Walking a lot.
- In summer, combine walking with swimming and cycling.
- In winter, combine walking with skating and skiing.
Vitamin B6 deficiency in obesity:
Patients with metabolic and alimentary obesity often have vitamin B6 deficiency. Since pyridoxine deficiency is endogenous, it is recommended:
- Ensure adequate vitamin B6 intake through food.
- Periodically administer courses of vitamin B6 at therapeutic doses (50-100 mg per day) for 2-4 weeks while following a reduced diet.
To assess the effectiveness of treatment, it is necessary to monitor not only body weight but also blood biochemical parameters characterizing lipid metabolism. Therefore, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician in a hospital or outpatient clinic.

SARMs for Fat Burning: Review and Selection
Have you heard of SARMs? These drugs have gained popularity in the athletic world due to their effectiveness and affordability. Originally sought after for muscle building, some SARMs are also excellent for fat burning.
The Evolution of SARMs for Weight Loss:
The first drug to demonstrate good weight loss results was Cardarine. However, with advances in science, more modern and effective analogs have emerged: Reverol, Aicar, and then Fitorine.
How SARMs for Fat Burning Work:
The mechanism of action of each SARM is unique, and you can read about it in the description of each drug. What they have in common is their high effectiveness in the fight against excess weight, confirmed by scientific research and positive reviews from athletes.
How to Choose the Best SARMs for Fat Burning:
Despite their common purpose – weight loss – each SARM has its own unique characteristics that will help you make the right choice:
- Aicar - its primary effect is increased endurance. Aicar is an excellent choice for those who enjoy cycling sports (running, swimming, triathlons, cycling, etc.), helping not only lose weight but also improve athletic performance.
- Reverol - it replaced Cardarine and surpassed it in effectiveness. If you're looking for a powerful fat burner, Reverol is an excellent option.
- Fitorine - a new generation of SARMs for fat burning. User reviews point to its superiority in the fight against excess weight. A distinctive feature of Fitorine is the removal of excess water from the body, which can be especially useful for achieving a lean body.

Benefits of SARMs for fat burning:
- Effectiveness in the fight against excess weight.
- Accelerated metabolism.
- Lowered cholesterol.
- No side effects typical of other fat burners (increased blood pressure, tremors, insomnia, etc.).
Note: Using SARMs requires careful study of the product information and consultation with a specialist. However, you can find information on our website in the SARMs section, in the Catalog. Keep an eye out for all the latest additions to our anabolic-androgenic steroid store. We sell all sports products, including SARMs!
————————————————————————————————————————
Thanks for reading, dear athletes!
As for the price of anabolic steroids, they vary on average and depend on the manufacturer. But with us, you can buy high-quality medications and supplements at the best prices with fast delivery throughout the US and Europe. Visit our official website, AnabolShop.org, and believe me, it’s worth it!
Subscribe to our news and article channel on Telegram!
- News - https://t.me/anabolshops
- Article channel - https://t.me/+sS0shaQLnmMwYTEy
We hope you enjoyed the article and thank you for reading.
Good anabolism to all athletes!
