Good day, dear friends! In today’s article, we’ll explore a very interesting and important topic for many athletes: diet for muscle gain!
This article will provide advice and explain the principles of diet planning, whether for mass gain, cutting, or other purposes.
Introduction:
Instead of chasing trendy, often absurd diets focus on proven bodybuilding nutrition principles. Forget horseradish, garlic, and purple vegetables! This article from the AnabolShop.org offers a guide based on scientific evidence and practical experience to help you create your own mass-gaining diet.
Who is it for?
This diet is universal and suitable for bodybuilders of any training level and with any amount of muscle mass. It can be followed indefinitely, with no specific «in» or «out» phases.
Key Principles:
- Realistic Approach: Forget complicated food combinations and a narrow food spectrum.
- Proven Methods: Adhere to the fundamental principles of bodybuilding nutrition.
- Gradual changes: Increase or decrease the amount of food you eat gradually to avoid metabolic imbalances and digestive problems. Give your body time to adapt.
Use these principles to create a diet that suits your needs and preferences.
Basic Principles for Diet
To effectively gain muscle mass, it’s essential to carefully plan your diet, taking several key principles into account. One of the most important is maintaining an optimal hydration regimen. During periods of intense muscle growth, metabolic processes accelerate, requiring increased water intake. Aim for 3-4 liters of fluid per day, including water from food. Never ignore your thirst to avoid dehydration.
Now about meal structure.
Modern research confirms that the anabolic effect of food lasts on average 3-4 hours, even when amino acid levels are high. Therefore, to achieve maximum muscle growth, it is recommended to eat 5-6 meals throughout the day. This ensures a steady supply of nutrients to the muscles without overloading the digestive system.
It is important that the majority of your diet (approximately 70%) consists of high-calorie foods. Fruits and vegetables are certainly healthy, but their proportion shouldn’t exceed 30%, as high fiber can hinder the digestion of high-calorie foods and reduce nutrient absorption.
Minimize the consumption of foods rich in saturated fats, such as fatty meats, sausages, and butter. Much of the fat consumed during a nutrient oversupply will be stored in fat cells. You should also avoid refined carbohydrates, especially sweets and baked goods, as they cause a sharp spike in blood sugar, which leads to its conversion to fat. An exception is the period after exercise, when muscles actively absorb glucose, and refined carbohydrates can promote the secretion of the anabolic hormone insulin, which is important for muscle growth.
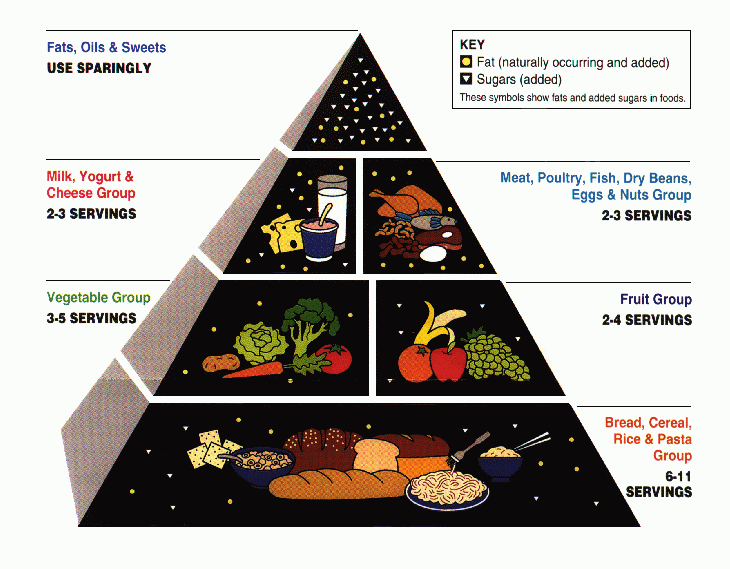
Food pyramid
Additional recommendations (from our sports consultant):
- First off, you should focus on high-quality protein. Include a source of high-quality protein (meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes) at every meal. Protein is the building block of muscle, and adequate intake is critical.
- Complex carbohydrates are your friend! Instead of quick-digesting carbs, choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, brown rice, and oatmeal. They provide stable energy levels and don’t cause sudden spikes in blood sugar.
- Don’t forget healthy fats. It includes healthy fats in your diet, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil. They are important for hormonal balance and overall health.
Monitor your progress: Regularly measure your weight, measurements, and monitor changes in the mirror. This will help you adjust your diet and training plan for optimal results.
By following these principles, you can effectively gain muscle mass while minimizing fat accumulation. Remember that nutrition is an integral part of the training process, and the right approach will help you achieve your desired results faster and more safely.
Friends, the ideal diet for muscle gain isn’t just about the number of calories, but also their proper distribution throughout the day, as well as a balanced ratio of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
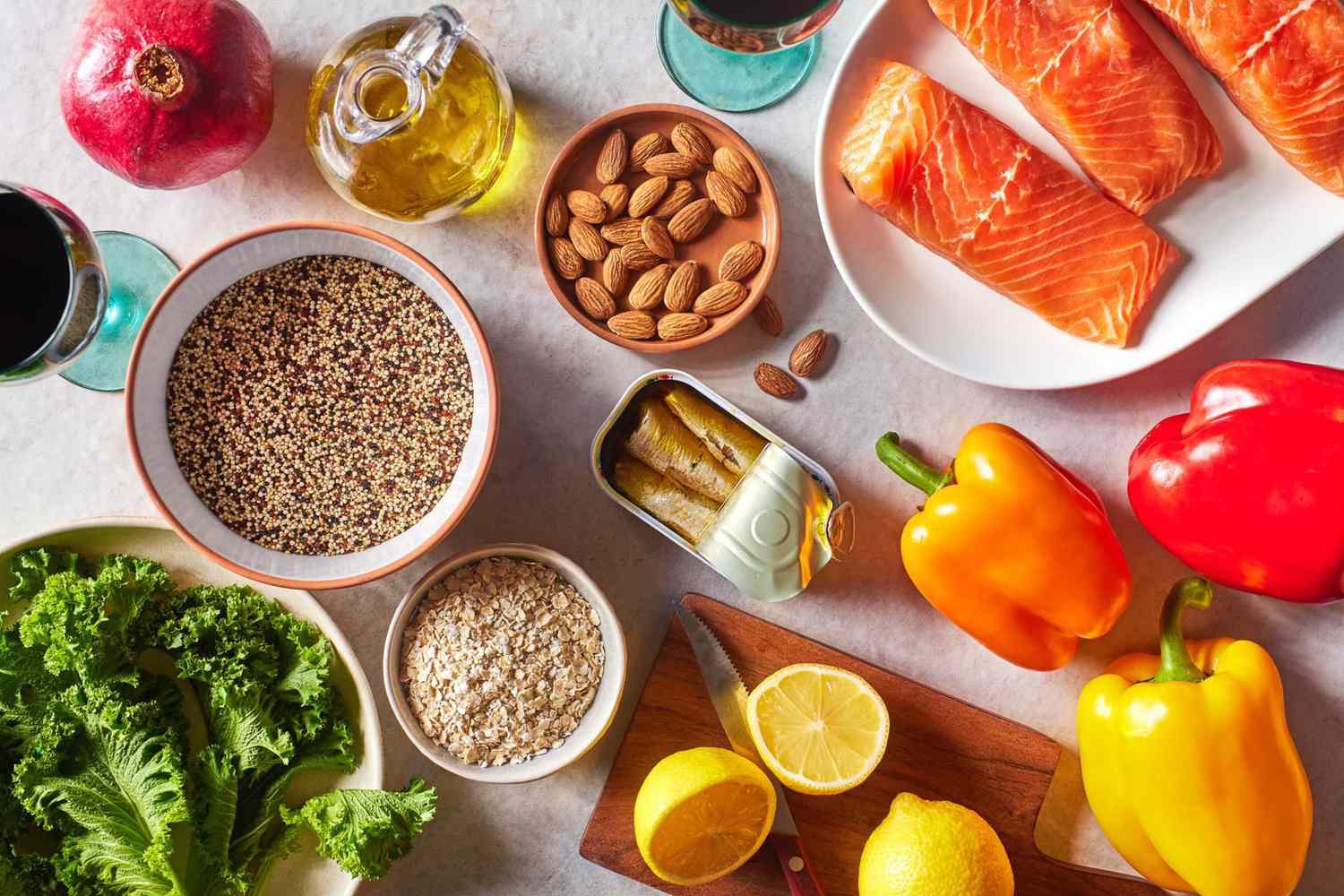

Nutrient Distribution:
Think about overall balance! Carbohydrates should make up 50-60% of your total calories. Focus on slow-digesting carbohydrates, which provide a steady energy level. Proteins should make up 30-35%; they are the key building blocks for muscle. Ideally, half of your protein should come from regular food, and the rest from sports nutrition. Fats should make up 10-20%. Don’t reduce your fat intake below 10%, as this can disrupt your metabolism. Choose vegetable fats and fatty fish, which are rich in beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
It’s important to remember that there’s no one-size-fits-all formula. Beginner athletes should experiment and find the optimal ratio that works best for them. The figures above are a starting point. Interestingly, these proportions are not significantly different from nutritionist recommendations for the general population, confirming their universality and benefits for both health and achieving fitness goals.
Meals and their importance:
Although recent research shows that daily portion distribution plays a secondary role, it is recommended to eat approximately 70% of all food in the first half of the day (before 4:00 PM). The total volume of food should be approximately the same at each meal.
Never eat sweets or fatty foods before bed. Food before bed should be easily digestible and rich in protein. Excellent choices include fermented milk products, vegetables, poultry, salads, eggs, and fish.
Be sure to eat for two hours before your workout. Include protein-rich foods and foods containing slow-release carbohydrates, such as cereals, flour products, and vegetables. Carbohydrates are essential for replenishing glycogen stores and providing energy to muscles and the brain during exercise. Amino acids help kick-start the anabolic process.
Post-workout: The body’s greatest need for nutrients is after a workout. It’s recommended to consume a carbohydrate-protein shake (gainer) immediately afterward, followed by a full meal rich in protein and slow-digesting carbohydrates no later than 1-1.5 hours later. You can add a small amount of fast-digesting carbohydrates (such as sweets). This opens the so-called protein-carbohydrate window, when the body is most receptive to digestion, directing nutrients toward muscle recovery and energy replenishment.
Practical advice (from a sports consultant):
Try calculating your protein needs. Use online calculators (such as FatSecret) or consult a nutritionist to determine your individual protein needs, considering your body weight, physical activity level, and other factors.
But don’t limit yourself to just one protein source. Include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and other protein-rich foods in your diet. Plan your meals in advance to avoid making unhealthy choices due to lack of time or opportunity.
And, of course, keep a food diary: Record everything you eat to track your calories, protein, fat, and carbohydrate intake. This will help you identify problem areas and make necessary adjustments to your diet.
By following these recommendations and listening to your body, you can create an effective and balanced diet that will help you achieve your desired muscle gain results.
Carbohydrates as a source of energy and muscle support:
Of all nutrients, carbohydrates are the most active in energy production. Building just 0.5 kg of muscle mass requires approximately 2,500 kilocalories - a huge amount of energy! Carbohydrates provide the body with clean energy, which it uses to support all functions, including muscle synthesis. Thus, carbohydrates allow the body to conserve protein, directing it to its primary function—the construction and repair of tissue, including muscle.
Carbohydrates and Fat Burning: An Inseparable Link:
Many people mistakenly believe that they need to eliminate carbohydrates to burn fat. In fact, carbohydrates are essential for effective fat burning. Through complex chemical reactions within cells, the body converts fat into energy. Carbohydrates act as a «match,» igniting the «wood» (fats) at the cellular level. If there aren’t enough carbohydrates at key stages of this process, fats won’t burn completely and efficiently but will simply «smolder.»
AND YES! The type of carbohydrates matters! Choose complex carbohydrates (oatmeal, brown rice, whole-grain bread) over simple carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods). Complex carbohydrates provide a stable energy level and don’t cause sharp insulin spikes.
And after a workout, it’s important to replenish glycogen stores, so consuming fast-acting carbohydrates in moderation can be beneficial. This will help restore energy and speed up muscle recovery. Carbohydrate needs depend on many factors, including activity level, training goals, and individual body characteristics. It’s important to experiment and find the optimal amount of carbohydrates for yourself.
Friends, remember that carbohydrates should be part of a balanced diet that includes sufficient protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals.

The key principle of muscle gain
The key principle of muscle mass gain boils down to one thing: energy surplus. Muscle grows only when the amount of energy consumed (in the form of food) exceeds the amount of energy expended by the body.
However, there’s an important nuance here. The body strives for homeostasis - maintaining a constant internal environment. This means that simply increasing caloric intake by 5%, 10%, or even 30% may not result in weight gain. The body can adapt to this increase without triggering muscle growth.
To get muscle mass off the ground, it’s sometimes necessary to significantly increase daily caloric intake—by 50% or even 100%!
How to determine the required food volume:
Use the following method to determine the optimal food volume for muscle mass gain:
- Gradually increase your caloric intake.
- Weigh yourself at least every three days.
- Aim for a weight gain of 600-800 grams per week. If the gain is less, eat more. If the gain is greater, reduce the amount of food.
- After a month, you can adjust your norm.
Equally important as building muscle mass is managing your body fat.
Regularly monitor your body fat percentage to avoid negative health consequences.
A 2015 study1 of 58 pairs of twins found that the active accumulation of dangerous visceral fat in men begins at 20.6% total body fat, while in women it begins at 39.4%.
Practical recommendations:
- If body fat reaches 15-20% in men, stop gaining weight and switch to a cutting diet.
- Gradually reduce body fat to 10%.
- Once body fat reaches 10%, you can begin a new bulking cycle.
This approach allows you to optimize muscle gain while minimizing excess fat accumulation and maintaining your health.
Important: Do not exceed a weight gain of more than 800 grams per week. Otherwise, your body will begin to store too much fat.
Protein Products:
Creating an optimal diet is an important task for any bodybuilder. A variety of foods containing essential nutrients not only helps you achieve your muscle-gain goals but also avoids monotony. When creating a menu, it’s important to remember that most foods contain proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Therefore, the breakdown below is tentative, focusing on the predominant nutrient. Try to regularly rotate foods and update your menu to avoid aversion to certain dishes.
Protein is the building block of muscle, so protein foods play an important role in a bodybuilder’s diet. Here is a list of the most popular and readily available protein sources:
| Product | Description |
| Lean meat | Poultry is preferable, as it contains virtually no fat and is easily digested. |
| Fish and seafood. | You can eat any fish, including fatty fish, at least 2-3 times a week. Fatty fish is rich in beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. |
| Dairy products. | Choose low-fat options. The most popular are cottage cheese, cheese, kefir, milk, yogurt, and others. |
| Eggs. | You can eat 6-8 eggs per day, including the yolks. It has been scientifically proven that if you don’t have high blood cholesterol, eggs won’t affect your cholesterol levels later. |
| Legumes. | Beans, peas, mung beans, and lentils are the main plant sources of protein, although their protein value is lower than that of animal products. Lentils and chickpeas also contain significant amounts of BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids).*** |
| Nuts. | They contain not only protein, but also valuable unsaturated fatty acids. |
***Important: Soy is not included in this list because soy products are often genetically modified, and men are advised against consuming soy due to its hormonal activity.

Carbohydrate Foods:
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for training and muscle growth. Choosing the right carbohydrate foods will help you achieve your goals.
1. Grains:
Porridges contain slowly digestible carbohydrates, protein, trace elements, and vitamins. The most beneficial porridges include buckwheat, barley (pearl barley), oatmeal, rice (preferably brown), millet, corn, wheat, and quinoa.
Pasta and Noodles: Choose products made from wholemeal flour and durum wheat. Eat bread mostly whole grain or brown bread.
And regarding cereals and muesli, you can add variety to your diet but choose low-sugar options.
2. Vegetables and Mushrooms:
Limit starchy vegetables such as potatoes, boiled or stewed carrots, and beets. Fresh vegetables are the most beneficial, as they contain the maximum amount of vitamins. They facilitate the digestion and absorption of animal protein and are a source of essential fiber, vitamins, and macro- and micronutrients. Mushrooms add aroma and flavor to dishes, but lack high nutritional value, as their protein is poorly digested.
3. Fruits and greens:
- Extremely healthy, containing many vitamins and minerals.
- Sweet fruits (grapes, pears, ripe bananas, persimmons) are high in simple sugars, so their consumption should be limited.
Pair vegetables with almost every protein meal to improve digestion and protein absorption. Choose complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index to ensure stable energy levels. Also, limit your intake of simple sugars, especially those found in sweet fruits.

Products with useful fat
Fats play an important role in hormonal regulation and overall health, so they shouldn’t be eliminated from your diet, even when building muscle mass.
Fat sources:
Use vegetable oil sparingly for salad dressings and cooking. Choose unrefined, extra-virgin oils, such as olive, flaxseed, sesame, and others.
Seafood is undoubtedly an important source of healthy fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega-3 fatty acids are recommended for supplementation to support cardiovascular health, improve cognitive function, and enhance overall well-being.
Combination with sports nutrition:
The diet described above can be used as a standalone nutrition strategy or in combination with sports nutrition and even anabolic steroids, if it suits your goals and you understand the risks.
- Take protein shakes between meals, before bed, immediately after waking up, and immediately after training to maintain high amino acid levels in the blood and stimulate muscle growth.
- Take a gainer an hour before and immediately after training to provide energy and restore glycogen stores.
- Take whey isolate after training for rapid recovery and stimulation of protein synthesis.
- Take BCAAs after training, as they have a strong evidence base.
- A vitamin and mineral complex is highly recommended, as bodybuilders’ diets often suffer from vitamin deficiencies due to insufficient fruit and green vegetable consumption.
- Take creatine after training with a sweet juice, gainer, or protein shake to improve absorption by muscles.
Combination with anabolic steroids:
Anabolic steroids themselves don’t change your diet, but they do allow you to consume significantly more food and accelerate muscle gain. Ideal muscle gains when using steroids are 1-1.5 kg per week, which is twice as much as with natural training.
Bonus! Protein Shake Recipe
From the AnabolShop.org team, we want to share with our readers the perfect recipe for enhanced mass gain for men. For effective muscle gain, try this signature protein shake, designed specifically for men.
You’ll need:
- 237 ml (1 cup) skim milk
- 119 ml (1/2 cup) calcium-fortified orange juice
- 21 g (1 tablespoon) honey
- 37 g (1/4 cup) frozen strawberries
- 21 g whey powder
- 5 ml (1 teaspoon) Brain Booster Omega-3 Powder
Mix all ingredients until smooth.
Nutritional information (per serving):
- 378 calories
- 54 grams carbohydrates
- 36 grams of protein
- 2 grams fat
- 1 gram dietary fiber
Food group servings:
- 1/2 serving fruit
- 1/2 serving lean protein
- 3 servings of very lean protein
- 1 serving skim milk
- 4 teaspoons added sugar
This shake is perfect for post-workout or as a snack between meals. It contains the optimal combination of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to support muscle growth and recovery.

Evidence of Effectiveness:
Our recommendations for consuming protein-carbohydrate shakes are based not only on personal experience but also supported by scientific research demonstrating their positive impact on athletes’ physical performance.
Numerous scientific experiments confirm that protein-carbohydrate shakes have a significant impact on hormonal balance and promote muscle growth. Here are a few examples:
1. A study on the effect of protein on insulin levels: In one study, participants (normal-weight men and women) followed a diet with varying protein contents (from 0 to 49.9 grams) combined with 58 grams of carbohydrates. The results showed that protein consumption resulted in higher insulin levels compared to a protein-free diet, demonstrating the «insulin-boosting» effect of protein.
2. A study on the effects of various post-workout supplements: In another experiment, experienced strength athletes were given water (for comparison), a carbohydrate supplement, a protein supplement, or a protein-carbohydrate shake immediately and two hours after training. Blood tests showed that the protein-carbohydrate shake caused the greatest increase in insulin and growth hormone (GH) levels. This highlights the synergistic effect of protein and carbohydrates in creating a hormonal environment favorable for muscle growth.

Regarding the purchase of the drug, it is available on our official website AnabolShop.org. Order all the drugs you are interested in directly from us!
For each drug, there is a detailed description of the effects, course, side effects and price with information on delivery. Thank you for reading. The drugs you are interested in are in the corresponding category in the store catalog. Starting from oral drugs, ending with injectable steroids, Growth Hormone and PCT drugs. Thanks for reading!
Good anabolism to all!
————————————————————
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26117000
